Mathematics and Design
Mathematics - Grade 10
This unit of inquiry is not a recipe book but rather a launchpad to inspire new BIG IDEAS. We encourage you to use and/or modify one, or several of the BIG IDEAS below. Adapt it to the grade/ ability level of your students.
Enduring Understanding
Mathematics and science are the foundation of engineering and design
Guiding Questions
How is mathematics utilized within the fields of design and engineering? What impact do science and mathematics play in designing and developing cost effective products for a global market?
Mind Opening
Choose or devise practices to encourage students to be open to new experiences and ways of thinking in your classroom. For example, the MindUP in-school program.
Discovery and Inspiration:
Launch the Project
• Introduce the Theme: Present the Enduring Understanding and Guiding Questions using vocabulary that is appropriate for your grade level.
• About Vancouver Biennale: Play a short video.
• Create Project Space: Brainstorm ideas to make the project theme visual and visible using bulletin boards, and/or a project corner to share relevant materials and inquiry questions and processes.
Reference Resources
• Introduction to Sculpture and Public Art Unit Plan for information on how art has evolved over time and the unique experience sculptures and/or public art brings
• Vancouver Biennale 2014-2016 Exhibition Theme: Open Borders / Crossroads Vancouver
• Vancouver Biennale Legacy: Jasper (John Clement, USA)
• About Artist and Artwork (PDF)
Other Resources
Metro Vancouver’s WhiteWater a global leader in wild water parks by Vancouver Sun
WhiteWater: The Waterpark and Attractions Company
Learning to Learn:
Art Inquiry
Visit Jasper and encourage students to explore the art piece at different angles individually and in groups. This Art Inquiry process enables the students to practice observing, describing, interpreting, and sharing visual information and personal experiences. Use the Art Inquiry Worksheet (PDF) to guide and capture their ideas and impressions. Customize or create your own Art Inquiry Worksheet as appropriate for your project and class needs.
Have students look at the materials, shape and form of the sculpture and facilitate a discussion relating to the guiding question. Start a discussion on the engineering process by taking measurements of the diameter and length of the sculpture to calculate the volume of the sculpture. Proceed to discussion on the artistic design process by sharing students’ perspectives on the aesthetic appeal of the assembled geometric shapes.
Shared Insights
• Sharing Art Inquiry Experience: Ask students to share the Art Inquiry Worksheet responses in class.
• Artist Themes – Research: In small groups students rotate between information stations detailing the artist’s life and work. Station topics include: (1) education and training; (2) lifetime of artwork; (2) materials and processes; (3) beliefs and values. At each station, students answer questions and complete a task. For example, at the station “life’s work” students might plot the artist’s various installations on a map of the world.
• Artist Themes – Engineering & Design: Ask the students to select a everyday product that they can relate to Jasper in term of shape, materials or form. Some possibilities include water park, playground equipment, or obstacle course. Have students work in group to discuss how mathematics and industrial design arts are applied in the product design process.
Inquiry Challenges
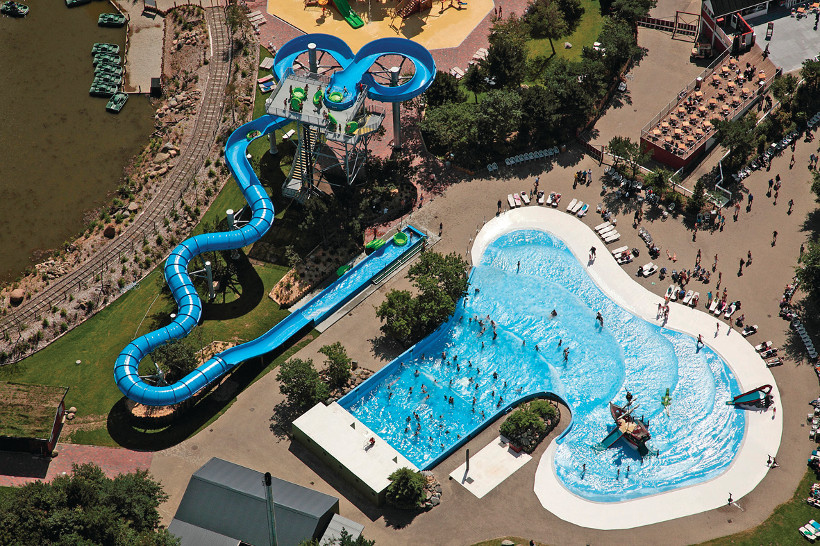
Water Slide Design Challenge: The largest waterpark company in the world is in the Lower Mainland. Since 1980 WhiteWater West Industries has built over 4,000 projects globally from hotel waterslides and community centre pools to outrageous installations with names like Rain Fortress, Whizzard, Master Blaster and Zoomerang, some reaching over 35 metres in height.
Most of WhiteWater’s booming business is international, including Bali Waterpark in Fushun, China, which is the largest in that country and Beijing’s Happy Magic Water Cube, which transformed the National Aquatics Centre built for the 2008 Summer Olympics. The Sunway Lagoon in Kuala Lumpur is one of the largest wave pools in the world, creating three-metre waves that some people surf on. Other innovative designs are found on cruise ships around the world.
Class Project: Students are to respond to a call for waterslide design submissions from a local waterpark company. The submission requirements are: (teacher to select materials: ie: rubber hose or tube cut in half, marble that fits into the tube, wooden chopsticks to use for supports)
Engineering Design Process: Work in groups of four to design a waterslide.
- Construct a scale model of the design (model should include a one metre drop, two metres of tube, two turns and three variations in slope).
- Test and adapt the model to ensure a marble can roll down the entire waterslide without bouncing (leaving the surface of the waterslide).
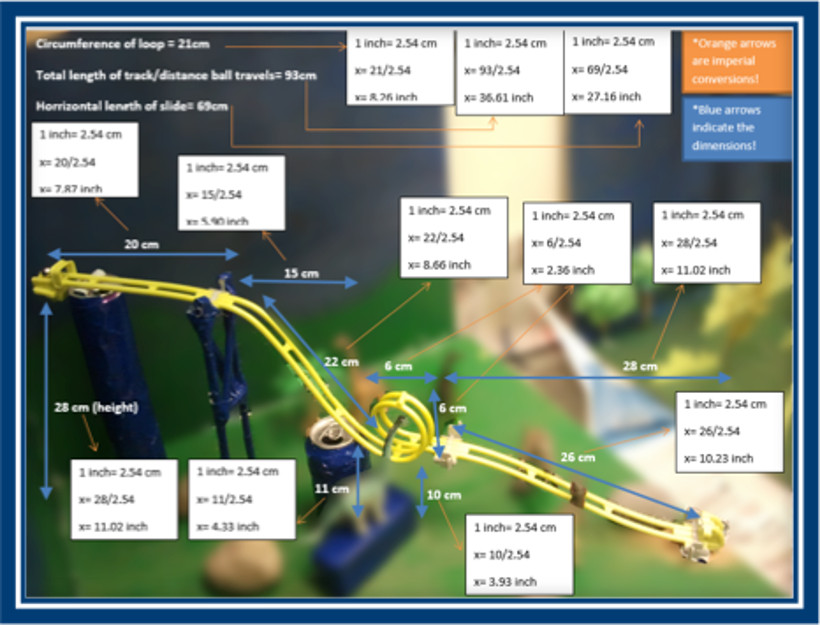
- Calculate the average slope of the slide, provide the horizontal, vertical and diagonal lengths in both the metric and imperial measurement systems, calculate the angle of depression and graph two relations connected to your waterslide.
Submission Checklist: Create a diorama (3D miniature scenic exhibit) that included the following items:
- Scale Model of the Waterslide – show proof of the test results that a marble can roll down the entire waterslide without bouncing (leaving the surface of the waterslide).
- Drawing of the Side View – Draw a side profile of the model and show the measurement of the vertical distance, the horizontal distance in both the metric and imperial measurement system (show conversions), use trigonometry to calculate the diagonal length and angle of depression.
- Average Slope – Calculate the slope at a variety of places on the waterslide, identify the steepest section and the least steep section and calculates the average slope.
- Graphing Relations – Recognize two relations involved in waterslides/waterparks, collect data and graph the relations. Ensure one of the relations is linear (describe and represent it using words, ordered pairs, tables of values, graphs, and equations). Show the domain and range for both relations.
- Proposed Materials and Colour – state reasons for the choice of colours and materials
- Final Product – All components put on the diorama in a presentable manner.
Contest Assessment Criteria:
- Visual appeal
- Sound and safe engineering design based on stated scientific and mathematical principles
- Presentation package
Student Creations and Taking Action
Teachers may use differentiated instruction and give students the option to present their projects using various visual presentation methods (powerpoint, video, prezi).
Students can organize a lunch time show and tell session to present their design proposals to other students for feedback and comments prior to submission or an in-school contest for favourite design.
Reflection
• Teacher and students can reflect on their entire learning process by revisiting the Enduring Understanding and relevant Guiding Questions.
• How did the unit of study open inquiry, create cross–curricular learning opportunities and/or apply learning to real life situations? Has this unit of inquiry changed your opinions, values and world view? In what ways, if any, has it helped you grow as a learner?
Ideas for Cross-Curricular Access
• Social Studies – Given the time period of study, identify three engineering design breakthroughs and explain the dependency of design and advancement and availability of materials. An example will be the Iron Bridge in England being the first arch bridge in the world to be made of cast iron, a material which was previously too expensive to use for large structures. A new blast furnace nearby lowered the cost and encouraged local engineers and architects to solve a long-standing problem of a crossing over the river. Steam engine is another example.
• Science – Application of Scientific Principles: Have students research and inquire into what scientific principles such as gravity, motion and simple machines are applied in the design of the waterpark. Investigate the functions of the machines required for the operation and safety factors consideration such as fire zone and in the choice of materials.
• Arts Education – Media: For submission presentation package: create videos to record the marble rolling down the waterslide scale model. Take professional photographs of the waterslide scale model and/or create animation video to simulate the form and function of the design.
Credits
Inspired by Grade 10 mathematics project by Kelly Skehill, Mathematics Teacher at West Vancouver Secondary School
Reviewed by Rosalind Poon, Teacher Consultant, Richmond School District
©2013 Vancouver Biennale